If your doctor has suggested keyhole surgery, you may hear two common terms: laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery. Both are modern, minimally invasive techniques that use small cuts instead of a large incision and help patients recover faster than open surgery.
However, they are not the same. This guide explains the difference between laparoscopic and robotic surgery in simple, easy-to-understand language.
What Is Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is also known as keyhole surgery. Instead of one large cut, the surgeon makes 2 to 4 small cuts. Through these cuts:
- A thin camera (laparoscope) is inserted
- Long surgical instruments are inserted
- The surgeon views the inside of the body on a screen and performs the surgery
- The surgeon directly controls the instruments by hand
Laparoscopic surgery is commonly used for:
- Gallbladder surgery
- Appendix surgery
- Hernia repair
- Gynecological surgeries
- Many abdominal procedures
Why Laparoscopic Surgery Is Commonly Used
Laparoscopic surgery is widely practiced because it offers:
- Smaller cuts with smaller scars
- Less blood loss
- Less pain compared to open surgery
- Faster recovery
- Shorter hospital stay
- Earlier return to routine activities
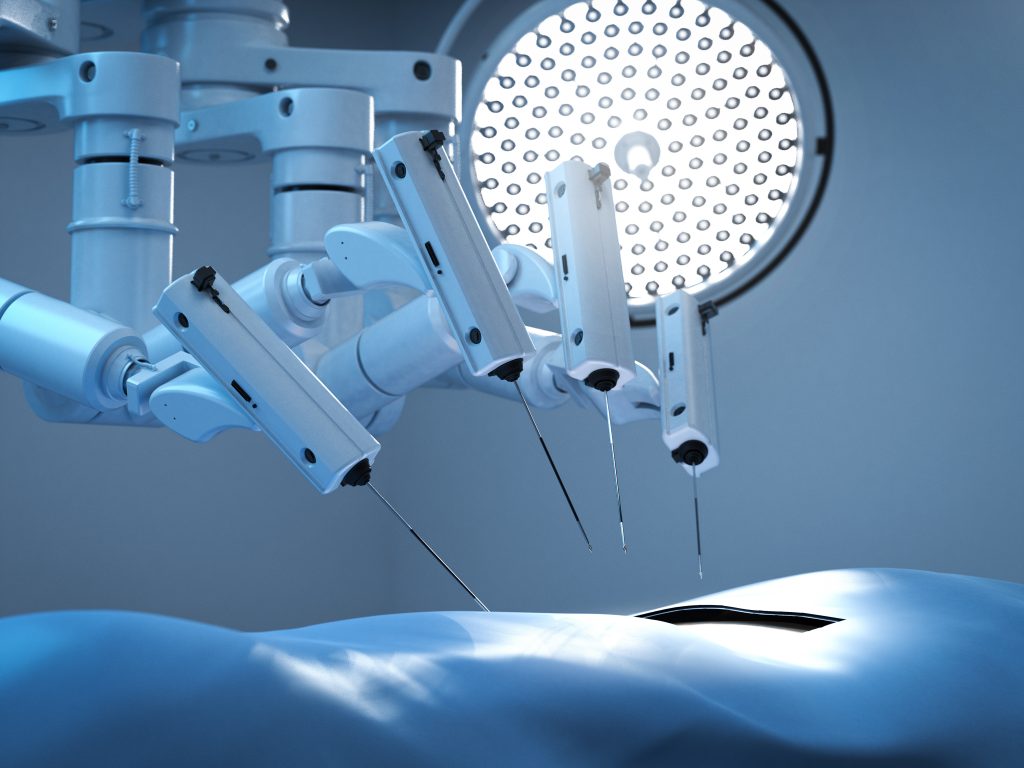
What Is Robotic Surgery?
Robotic surgery is also minimally invasive, but the surgeon uses a robotic system to control the instruments.
Important Point: The robot does not perform surgery on its own. Every movement is controlled by the surgeon in real time.
How Robotic Surgery Works
- The surgeon sits at a console
- The surgeon controls robotic arms holding tiny instruments
- The instruments move with very high precision
- The surgeon sees a high-definition, magnified 3D view
- Instruments can bend and rotate like a human wrist
This allows precise movements, especially in tight or delicate areas.
Why Robotic Surgery Is Used in Certain Cases
Robotic surgery provides the surgeon with:
- Better visibility
- Better control
- Higher precision for complex or delicate procedures
- Improved comfort during long surgeries (better ergonomics)
This can be helpful in surgeries that require very fine and accurate movements.
Robotic Surgery vs Laparoscopic Surgery – Simple Comparison
| Feature | Laparoscopic Surgery | Robotic Surgery |
| Type of surgery | Minimally invasive (keyhole surgery) | Minimally invasive with robotic assistance |
| How it is done | Surgeon operates using long instruments by hand | Surgeon controls robotic arms from a console |
| Who performs the surgery | Surgeon directly handles instruments | Surgeon controls the robot (robot does NOT act on its own) |
| Cuts / Incisions | Small cuts (usually 2–4) | Small cuts (similar size to laparoscopy) |
| View inside the body | 2D camera view (in most cases | High-definition, magnified 3D view |
| Precision of movement | Good precision | Very high precision, smooth and steady movements |
| Instrument flexibility | Limited movement of instruments | Instruments bend and rotate like a human wrist |
| Surgeon comfort | Surgeon stands for long hours | Surgeon sits comfortably, reducing fatigue |
| Pain after surgery | Less than open surgery | Similar or sometimes even less |
| Blood loss | Minimal | Often minimal or further reduced |
| Scars | Small scars | Small scars |
| Recovery time | Faster than open surgery | Often similar or slightly faster in selected cases |
| Hospital stay | Short stay | Short stay |
| Best suited for | Common and straightforward procedures | Complex, delicate, or precision-demanding procedures |
| Cost factor | Generally lower | Usually higher due to advanced technology |
Benefits of Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery includes all advantages of minimally invasive surgery and may additionally offer:
- Greater precision for complex surgeries
- Enhanced vision through magnified 3D imaging
- Steadier movements with reduced hand tremors
- Potential for less blood loss and faster healing in selected cases
Note: Outcomes depend on the type of surgery and individual patient factors.
Which Surgeries Use These Techniques?
Both laparoscopic and robotic approaches are used in:
- General surgery – hernia, gallbladder, appendix
- Gynecology – fibroids, hysterectomy, endometriosis
- Urology – prostate and kidney surgeries
- Oncology – selected cancer surgeries suitable for minimally invasive methods
Your surgeon will advise the safest and most suitable option for your condition.
Who Can Choose These Surgeries?
The choice depends on:
- Overall health
- Previous abdominal surgeries
- Body structure
- Severity and stage of the condition
- Urgency of surgery
The goal is always safe surgery and the best possible outcome.

We Cure With Care
Being advised surgery can feel stressful. At Vasavi Hospitals, our specialists ensure you receive clear explanations, honest advice, and compassionate care from consultation to recovery.
Call 080 71 500 500 to book your consultation at Vasavi Hospitals.